Revolutionizing Food Evaluation: Food Compass 2.0 Enhances Healthfulness Assessment
The escalating health burdens of diet-related non-communicable diseases have prompted the development of innovative population-level strategies. Nutrient profiling systems (NPSs) have emerged as crucial tools for governments, industries, and stakeholders to promote healthier eating habits. The revised Food Compass 2.0 offers a comprehensive and validated approach to evaluating the healthfulness of diverse foods, beverages, and meals, addressing the limitations of previous systems.Unlocking the Potential of Holistic Food Evaluation
Addressing the Shortcomings of Existing Nutrient Profiling Systems
Many existing NPSs have faced significant limitations, including a narrow focus on negative nutrients, lack of assessment for various food ingredients or emerging nutrients, and inconsistent scoring across food categories and mixed products. To address these challenges, the original Food Compass was developed in 2021, capturing a holistic range of product characteristics, including nutrient ratios, food ingredients, processing attributes, and additive characteristics.Introducing Food Compass 2.0: Enhancing the Assessment of Healthfulness
Building upon the strengths of the original framework, the researchers have now presented Food Compass 2.0, an improved NPS that incorporates new data and the latest diet-health evidence. The updates include broader discrimination in scoring of food processing, inclusion of added sugar as a major energy source, increased scoring weight for dietary fiber, and lower scoring weight for dairy fat. Additionally, the new system features comprehensive data collection on artificial additives, which were previously unscored due to insufficient information.Validating the Improved Nutrient Profiling System
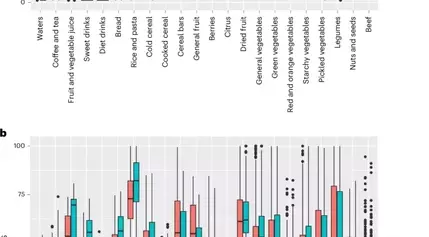
The researchers have thoroughly validated Food Compass 2.0 against health outcomes in a nationally representative population of US adults. The energy-weighted average Food Compass score (i.FCS) of individuals' diets was found to correlate strongly with the Healthy Eating Index-2015, a validated measure of a healthy dietary pattern. Furthermore, higher i.FCS was associated with more favorable cardiometabolic risk factors and a lower prevalence of chronic conditions, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and lung disease. The updated i.FCS also demonstrated a significant association with lower all-cause mortality.Enhancing Differentiation and Alignment with Dietary Guidelines
The revisions to Food Compass 2.0 have resulted in meaningful changes in the scoring of various food categories. The system now provides higher scores for minimally processed animal-based foods, such as seafood, dairy, meat, poultry, and eggs, while assigning lower scores to processed cereals, beverages, flavored yogurts, and processed plant-based alternatives. These updates better align the scoring with dietary guidelines and the latest scientific evidence on the health effects of different food processing levels.Promoting Healthier Food Choices and Reformulation
The researchers encourage the use of Food Compass 2.0 by researchers, policymakers, retailers, manufacturers, and all stakeholders interested in identifying and encouraging healthier food and beverage options. The comprehensive and validated nature of the system is expected to have global relevance, with ongoing efforts to adapt it for use in different world regions. The researchers also aim to develop and evaluate adaptations of Food Compass that can leverage commonly available nutrient and ingredient information, facilitating the scoring of all products in the marketplace.Empowering Informed Decisions and Driving Positive Change
By providing a robust and holistic assessment of food and beverage healthfulness, Food Compass 2.0 empowers consumers, policymakers, and industry to make more informed decisions and drive positive changes in the food landscape. The system's ability to differentiate products within and across categories, as well as its alignment with modern nutrition science and diverse food cultures, positions it as a valuable tool for promoting healthier eating habits and addressing the pressing public health challenges posed by diet-related non-communicable diseases.New

Lifestyle

Entertainment

Entertainment

Entertainment